Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Yukio*; Tsukiyama, Toshihisa*
Shahei Kaiseki No V&V Gaidorain Sakutei Ni Mukete, p.4 - 8, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita; Yee-Rendon, B.; Katano, Ryota; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Sasa, Toshinobu; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Research 2021-012, 58 Pages, 2022/01
A radiation shielding analysis was performed for the structure located above the spallation target of an accelerator-driven system (ADS), assuming one cycle of an 800 MW thermal and 30 MW beam power operation. In this analysis, the Monte Carlo particle transport code PHITS and the activation analysis code DCHAIN-PHITS were used. The structures to be analyzed are a beam duct above the target, a beam transport room located above the ADS reactor vessel, beam transport equipment, and the room ceiling. For each structure, the radiation doses and radioactivities during and after the operation were estimated. Furthermore, the shielding structure of the ceiling was determined. As a result, it was found that the radiation dose at the site boundary would be sufficiently lower than the legal limit by applying the determined shielding structure. Moreover, under the condition of this study, it was shown that the effective dose rate around the beam transport equipment positioned above the target after the operation exceeded 10 mSv/h, and that the maintenance and replacement of the equipment in the room would require remote handling.
Yamauchi, Michinori*; Nishitani, Takeo; Nishio, Satoshi
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 80(11), p.952 - 954, 2004/11
Considering the geometrical characteristics of tokamak reactors with low aspect ratio, a basic neutronics strategy was derived to construct the inboard structure mainly for neutron shielding and produce enough tritium in the outboard blanket. The designs for optimal inboard shield were surveyed and necessary thickness was estimated to make the neutron flux low enough on the super-conducting magnet. In addition, the outer blanket designs were studied to attain the tritium breeding ratio (TBR) large enough for a self-sustaining fusion reactor on the basis of the advanced fusion reactor materials.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kudo, Yusuke; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2141 - 2150, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.49(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dominant issue for the the modification program of JT-60 (JT-60SC) is to demonstrate the steady state reactor relevant plasma operation. Physics design on plasma parameters, operation scenarios, and the plasma control method are investigated for the achievement of high- . Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
. Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
Noda, Kimio; Shinohara, Kunihiko; Kanamori, Masashi
JNC TN8410 2001-010, 35 Pages, 2000/10
We, the radiation control section of JNC have had two important experiences on the JCO critical accident and the JNC fire-explosion accident. Especially, at the critical accident in JCO, it was essential to take an action on the radiation protection activities for the evacuated neighboring inhabitants to the safety area. During the accident, we carried out the radiation protection activities, at the beginning of the accident, environmental monitoring of the surrounding area. Especially for the JCO accident, we took an action to terminate criticality, radiation shielding and monitoring, environmental monitoring, radiation survey of the residents, radiation monitoring of exhaust air.
Takemura, Morio*
JNC TJ9450 2000-002, 112 Pages, 2000/03
This report is intended to make it easier to apply the measured data obtained from the Gap Streaming Experiment, which was conducted at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) during about two months beginning at the start of March, 1992 as the sixth one of a series of eight experiments planned for the Japanese-American Shielding Program for Experimental Research (JASPER) which was started in 1986. For this reason. the information presented includes specifications and measurement data for all configurations, compositions of all materials, characteristics of the measurement system. and daily-basis records of measurements. The Gap Streaming Experiment was planned to obtain the data of neutron streaming characteristics in the inclosure system above the core of an advanced fast reactor for verification and improvement of the analysis method to be applied to the shielding design. A iron-lined solid or slit concrete assembly was placed, with or without a spectrum modifier forming soft incident neutron spectrum, behind the TSR-II reactor of Tower Shielding Facility. Inserting central cylinders and cylindrical sleeves gave various gap width and offset in the slit concrete assembly. Neutron flux was measured behind the configurations with various types of detectors. The integral neutron flux in wide energy region was measured on radial traverse and on the axis behind the concrete assembly in almost all configurations. Neutron spectrum and fine radial distribution in high energy region was measured further in case of hard incident neutron spectrum, Information presented in this report is based mainly on a report issued by ORNL (ORNL/TM-12140. "Measurements for the JASPER Program Gap Streaming Experiment"). Additional information reported by the assignee is utilized also.
Mori, Tomoaki*; Takemura, Morio*
JNC TJ9450 2000-001, 96 Pages, 2000/03
This report is intended to make it easier to apply the measured data obtained from the Special Materials Experiment, which was conducted at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) during about a month beginning at the end of June, 1992 as the last one of a series of eight experiments planned for the Japanese-American Shielding Program for Experimental Research (JASPER) which was started in 1986. For this reason. the information presented includes specifications and measurement data for all configurations, compositions of all materials, characteristics of the measurement system. and daily-basis records of measurements. The Special Materials Experiment was planned to obtain the data of neutron attenuation characteristics of selected shielding materials for use in advanced fast reactors. The material of particular interest for the experiment was zirconium hydride that is rich in hydrogen. The mockup slabs for the special materials were preceded by the spectrum modifier behind the TSR-II reactor of Tower Shielding Facility. The layer of zirconium hydride was simulated with a combination of zirconium and polyethylene slabs. The thick layer of polyethylene with no zirconium was installed in some configurations.Neutron flux was measured behind the configurations with various types of detectors. The integral neutron flux in wide energy region was measured in eight configurations and neutron spectrum in high energy region was measured also in almost all configurations. Information presented in this report is based mainly on a report issued by ORNL (ORNL/TM-12277. "Measurements for the JASPER Program Special Materials Experiment"). Additional information reported by the assignee is utilized also.
*; Takemura, Morio*
JNC TJ9440 2000-005, 157 Pages, 2000/03
With use of the two-dimensional discrete ordinates code DORT and the standard groupwise shielding design library JSSTDL produced from the latest evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-3.2, experimental analyses for the representative configurations in the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment of the JASPER were performed. The results were compared with those obtained with use of traditional method DOT3.5/JSDJ2 for the previous JASPER experimetal analyses. In general, the change of the cross section library gives higher results and the change of the transport code gives lower results. Finally the new analysis method gives better agreement with the experimental results and also less deviations of calculational errors between various detectors. Experimental analyses for the thick concrete configulation in the Gap Streaming Experiment of the JASPER was also performed with the new analysis method, after solving the poor agreement found in last year with the original JASPER experimental analyses. The same tendency due to the library change was confirmed with the above mentioned analyses of the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment. Compilation of the input data necessary for future reanalyses of important configurations in JASPER experiments were continued through the above-mentioned experimental analyses and related informations were added for repletion of the database preserved in a computer disk holding previously accumulated data. Input data descriptions were made for auxiliary routines needed for the experimental analyses and their sample data were compiled and stored in the database.
Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; TRAN DUC PHI OAN*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-056, 487 Pages, 2000/02
JNC presented the 2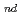 progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named TRAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named TRAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; TRAN DUC PHI OAN*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-055, 49 Pages, 2000/02
JNC presented the 2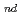 progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named THAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named THAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
Sawamura, Sadashi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-053, 41 Pages, 2000/02
Dose evaluation for direct radiation and skyshine from nuclear fuel facilities is one of the environment evaluation items. This evaluation is carried out by using some shielding calculation codes. Because of extremely few benchmark data of skyshine, the calculation has to be performed very conservatively. Therefore, the benchmark data of skyshine and the well-investigated code for skyshine would be necessary to carry out the rational evaluation of nuclear facilities. The purpose of this study is to obtain the benchmark data of skyshine and to investigate the calculation code for skyshine. In this fiscal year, the followings are investigated; (1)To improve the detection sensitivity of pulsed neutron measurement, two neutron detectors and some electronic circuits are added to the system constructed last year. (2)To estimate the neutron dose at the distant point from the facility instead of the commercialized rem-counter, a  He detector with paraffin moderator is equipped to the system. (3)Using the new detection system, the skyshine of neutrons from 45Mev LINAC facility was measured in the distance up to 300m. The results show that the time structure of pulsed neutrons almost disappears at the further points than 150m. (4)In the distance from 90m to 300m ordinal total counting method without gate pulse are applied to detect the neutrons. (5)The experimental results of space dependency up to 300m is fitted fairly well by the Gui's response function.
He detector with paraffin moderator is equipped to the system. (3)Using the new detection system, the skyshine of neutrons from 45Mev LINAC facility was measured in the distance up to 300m. The results show that the time structure of pulsed neutrons almost disappears at the further points than 150m. (4)In the distance from 90m to 300m ordinal total counting method without gate pulse are applied to detect the neutrons. (5)The experimental results of space dependency up to 300m is fitted fairly well by the Gui's response function.
*; *; Tanai, Kenji
JNC TN8400 99-048, 85 Pages, 1999/11
This paper reports the results of design analysis and trial manufacturing of full-scale titanium-carbon steel composite overpacks. The overpack is one of the key components of the engineered barrier system, hence, it is necessary to confirm the applicability of current technique in their manufacture. The required thickness was calculated according to mechanical resistance analysis, based on models used in current nuclear facilities. The Adequacy of the calculated dimensions was confirmed by finite-element methods. To investigate the necessity of a radiation shielding function of the overpack, the irradiation from vitrified waste has been calculated. As a result, it was shown that shielding on handling and transport equipment is a more reasonable and practical approach than to increase thickness of overpack to attain a self-shielding capability. After the above investigation, trial manufacturing of full-scale model of titanium-carbon steel composite overpack has been carried out. For corrosion-resistant material, ASTM Grade-2 titanium was selected. The titanium layer was bonded individually to a cylindrical shell and flat cover plates (top and bottom) made of carbon steel. For the cylindrical shell portion, a cylindrically formed titanium layer was fitted to the inner carbon steel vessel by shrinkage. For the flat cover plates (top and bottom), titanium plate material was coated by explosive bonding. Electron beam welding and gas metal arc welding were combined to weld of the cover plates to the body. No significant failure was evident from inspections of the fabrication process, and the applicability of current technology for manufacturing titanium-carbon steel composite overpack was confirmed. Future research and development items regarding titanium-carbon steel composite overpacks are also discussed.
*; *; Tanai, Kenji
JNC TN8400 99-047, 54 Pages, 1999/11
This paper reports on the design process for a carbon-steel overpack as a key component in the engineered barrier system of a deep geological repository described in the 2nd progress report. The results of the research and development regarding design requirements, configuration, manufacturing and inspection of overpack are also described. The concept of a composite overpack composed of two different materials is also considered. First, the design requirements for an overpack and presume environmental and design conditions for a repository are provided. For a candidate material of carbon steel overpack, forging material is selected considering enough experience of using this material in nuclear power boilers and other components. Second, loading conditions after emplacement in a repository are set and the pressure-resistant thickness of overpack is calculated. The corrosion thickness to achieve an assigned 1000 year life time and the required thickness to prevent radiolysis of ground water which might enhance corrosion rate are also determined. As aresult, the total required thickness of a carbon-steel overpack is conservatively estimated to 190 mm. This is a reduction of about 30% from the previous estimate provided in the 1st Progress Report. Additional items that must be considered in manufacturring and operating overpacks (i.e. sealing of vitrified waste, examination of main body and sealing welding, mechanism of handling) are evaluated on the basis of current technology, specific future data needs are identified. With respect to the concept of composite overpack (i.e., an outer vessel to provide corrosion-allowance or corrosion-resistant performance and an inner vessel to provide pressure-resistance), the differences in design concepts between the carbon-steel overpack and such composite overpacks are analyzed. Future data needs and analytical capabilities with respect to overpacks are also summarized.
Miya, Naoyuki; Kikuchi, Mitsuru; Ushigusa, Kenkichi; ; Nagashima, Keisuke; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Tobita, Kenji; ; Masaki, Kei; Kaminaga, Atsushi; et al.
JAERI-Research 98-012, 222 Pages, 1998/03
no abstracts in English
Takemura, Morio*
PNC TJ9055 97-001, 112 Pages, 1997/03
With use of a standard groupwise shielding design library JSSTDL produced from the latest evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-3.2, experimental analyses for the Axial Shield Experiment (homogeneous and central blockage type shield configurations with B C or stainless steel shield material) were performed. The results were compared with those obtained by the same analysis method and input data using JSDJ2 library that had been applied consistently to the JASPER experiment analyses. In general, the results with JSSTDL analyses are higher than those by JSDJ2 as were found in analyses in last year for the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment and the Special Materials Experiment. Consideration was made on the discrepancies between JSSTDL and JSDJ2 analysis results of the Axial Shield Experiment and also those of the sodium configulation in the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment. The former was done by exchange of macro cross section of each region, and the latter forcused on sodium cross section was done with use of cross section sensitivity analysis method. Compilation of the input data necessary for future reanalyses of important configurations in JASPER experiments, that were selected in previous study in last year, were continued and new data were added into the computer disk holding previous ones.
C or stainless steel shield material) were performed. The results were compared with those obtained by the same analysis method and input data using JSDJ2 library that had been applied consistently to the JASPER experiment analyses. In general, the results with JSSTDL analyses are higher than those by JSDJ2 as were found in analyses in last year for the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment and the Special Materials Experiment. Consideration was made on the discrepancies between JSSTDL and JSDJ2 analysis results of the Axial Shield Experiment and also those of the sodium configulation in the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment. The former was done by exchange of macro cross section of each region, and the latter forcused on sodium cross section was done with use of cross section sensitivity analysis method. Compilation of the input data necessary for future reanalyses of important configurations in JASPER experiments, that were selected in previous study in last year, were continued and new data were added into the computer disk holding previous ones.